Fatty liver is one of the most common liver diseases in Hong Kong. Studies show that over one-quarter of adults in Hong Kong suffer from fatty liver. Meanwhile, 1 in 5 non-obese individuals is found to have fatty liver.
In Asia, the number of fatty liver patients is rapidly increasing! A long-term high-sugar, high-fat diet, lack of exercise, coupled with stress and poor sleep quality, causes many to unknowingly develop fatty liver. Research shows that sitting more than 8 hours a day increases the risk of fatty liver by 44%! Lifestyle habits have a profound impact on liver health.
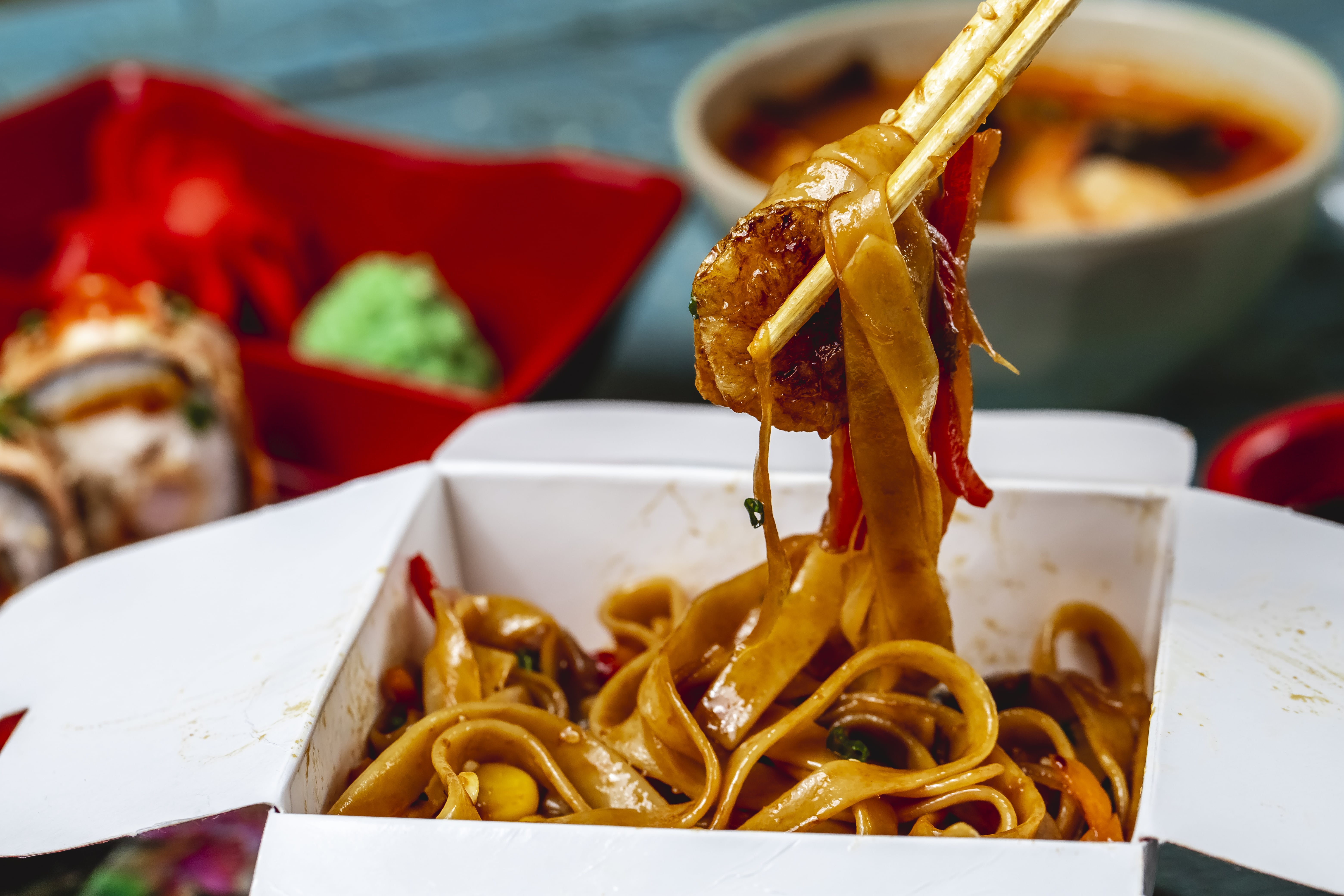

Hidden Risks of Takeout
Relying on takeout often may unknowingly increase the risk of fatty liver:
1. High in oil and fat: increases fat accumulation in the liver
Takeout is often deep-fried or cooked with heavy oil, such as fried chicken, fried rice, curry rice, etc., which causes daily fat intake to far exceed recommended levels. When the body cannot fully metabolize fat, the excess is stored in the liver, forming fatty liver.
2. Hidden sugars: increases fat synthesis
Many takeout items like sauces, beverages, and desserts contain large amounts of sugar (such as high fructose corn syrup). These sugars are metabolized in the liver and converted into fat stored in the liver.
3. High sodium content: causes water retention and increases liver stress
To enhance flavor and preserve food, takeout meals often contain high amounts of salt and MSG. Excess sodium intake can cause water retention and increase metabolic burden, further harming liver function.
4. Lack of dietary fiber: gut imbalance indirectly affects the liver
Takeout usually lacks vegetables or whole grains. Insufficient fiber intake leads to gut microbiota imbalance and promotes inflammation, which indirectly affects liver health.
5. High in calories but low in nutritional density: leads to obesity
Long-term dependence on takeout leads to excessive calorie intake (e.g., refined carbs, trans fats), increasing the risk of obesity and insulin resistance — the main causes of fatty liver.
Causes of Fatty Liver and High-Risk Groups
Common causes include:
- Long-term high-fat, high-sugar diet (e.g., frequent takeout )
- Lack of exercise, sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity, especially abdominal obesity
- High blood lipids or blood sugar
- Genetics and age factors
- Sleep deprivation or irregular lifestyle
High-risk individuals include:
- Office workers aged 30 and above
- Frequent drinkers or social drinkers
- People with a history of diabetes, hypertension, or high cholesterol
- Women undergoing hormonal changes after menopause
Does Fatty Liver Have Symptoms? Watch Out for These Early Signs!
Fatty liver often has no obvious symptoms in the early stage, causing many patients to miss the golden window for treatment. However, if it worsens, the following signs may occur:
- Discomfort or bloating in the upper abdomen
- Fatigue, lack of energy
- Poor appetite, nausea
- Unusual weight gain or loss
- Abnormal liver function tests (ALT, AST)
If fatty liver progresses further, it may lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer, with more severe symptoms such as:
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Ascites, swelling in lower limbs
- Nosebleeds, bleeding gums
- Palmar erythema, spider angiomas
What Happens if Fatty Liver is Left Untreated?
Many people mistakenly think that fatty liver is a “benign” condition, but in fact, it can develop into the following diseases and pose serious health threats:
| Fatty Liver Stage | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Liver Inflammation | Pain in the upper right abdomen, occasional fever, or no symptoms |
| Fibrosis | No obvious symptoms, or mild liver function abnormalities |
| Cirrhosis | Abdominal bloating, jaundice, leg swelling, skin itching, poor appetite, etc. |
| Liver Failure | Rapid weight loss, diarrhea, poor appetite |
Fatty liver can lead to cirrhosis and increase the risk of liver cancer. If the liver stores too much fat, it can damage cells and cause hepatitis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer. Controlling fatty liver early helps reduce the risk of worsening and developing into liver cancer!

5 Effective Ways to Reverse Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is a reversible disease. The key is early intervention and consistent lifestyle changes. Here are 5 recommended improvement methods:
1. Manage weight and abdominal fat
- Losing 0.5–1 kg per week is most effective; avoid rapid weight loss
- Body fat percentage, BMI, and waist circumference matter more than weight
2. Balanced diet with low sugar and low fat
- Reduce intake of sugar, fat, and refined starch
- Increase dietary fiber and quality protein (beans, fish)
- Limit red meat and processed foods
3. Exercise at least 3 times per week
- Combine aerobic exercise (e.g. brisk walking, swimming) with resistance training (e.g. weight training)
- Each session should be more than 30 minutes, at least 3 times per week
For busy and sedentary individuals, exercising 3 times a week may be challenging. Try walking a few extra flights of stairs or getting off one stop earlier — these are simple, feasible ways to move more. Any movement helps reduce fatty liver risk.
4. Quit alcohol and get adequate sleep
- Alcohol increases liver burden; it’s recommended to quit drinking
- Maintain 7–8 hours of sleep per night
5. Regular check-ups and liver function monitoring
- It is recommended to have liver function and fat index blood tests every 6 months
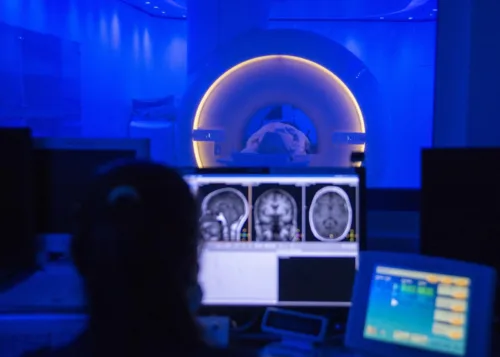
- Consider abdominal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for further assessment
How to Check for Fatty Liver?
To accurately diagnose and monitor fatty liver, the following are common and effective methods:
| Check-up Item | Details and Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Liver Function Blood Test | Checks for abnormal levels of liver enzymes such as ALT and AST |
| Liver Ultrasound Scan | Non-invasive and convenient; effective for detecting moderate to severe fatty liver but less sensitive for mild cases; suitable for initial liver evaluation |
| MRI Scan | Non-invasive with high accuracy; provides detailed assessment of liver condition, including mild fatty liver; shows fat distribution within the liver for targeted diagnosis and advice; ideal for those seeking detailed evaluation or with diagnosed fatty liver |
Reversing Fatty Liver Starts Today
Fatty liver is not only a concern for overweight individuals; it is a lifestyle-related condition. Regardless of whether you have obvious symptoms now, frequent consumption of high-fat takeaway meals and prolonged sedentary behavior may silently lead to fatty liver.
Concerned about your liver health? Consider scheduling a comprehensive health check that includes an MRI scan for precise assessment. Early detection of fatty liver helps you monitor and manage your liver condition effectively.
Fortunately, early-stage fatty liver is reversible. By taking prompt actions such as improving your diet, maintaining regular exercise, getting adequate rest, and undergoing periodic health checks, you can effectively reverse the condition and reduce the risk of progression to liver fibrosis or liver cancer.
Sources:
1. Kim D et al. (2022). Physical Activity Is Associated With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Significant Fibrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
2. The Chinese University of Hong Kong. CUHK Estimates One Million Hong Kong People are Suffering from Fatty Liver Disease.
3. CUHK Liver Care Centre. Diagnosed with Fatty Liver: Causes and Treatments
4. Hello Doctor. Four Stages of Liver Disease: Inflammation, Fibrosis, Cirrhosis, Liver Failure
5. CUHK Liver Care Centre. Diet, Exercise, Medication, Surgery: Four Ways to Improve Fatty Liver
6. Liver Disease Prevention and Treatment Research Foundation. Excessive Drinking… Be Careful of Fatty Liver and Liver Failure!