Locations:
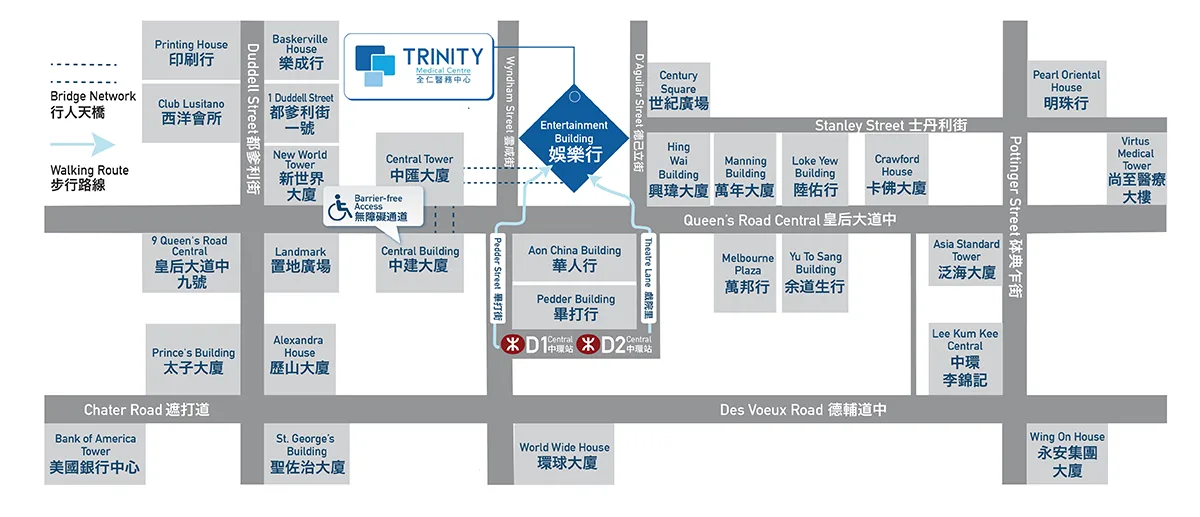
Central Diagnostic & Medical Centre
22/F , Entertainment Building,
30 Queen’s Road Central, Central
- Mon – Fri: 9:00 – 18:00
- Sat: 9:00 – 17:00
- Sun & Public Holiday: Closed
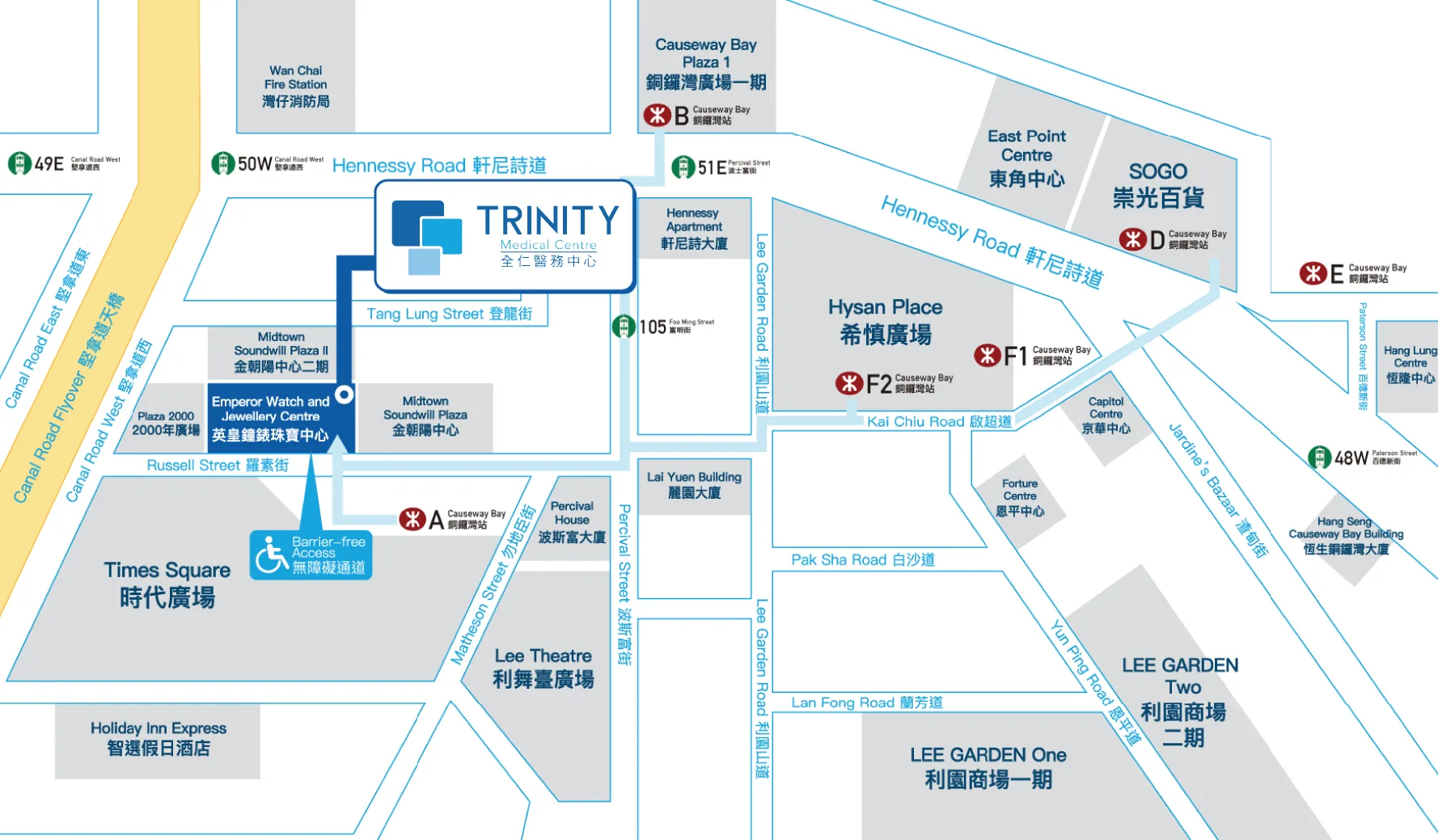
Causeway Bay – Trinity Diagnostic & Medical Centre
20/F Emperor Watch and Jewellery Centre,
8 Russell Street, Causeway Bay, Hong Kong
- Mon – Sat: 9:00 – 18:00
- Sun & Public Holiday: Closed
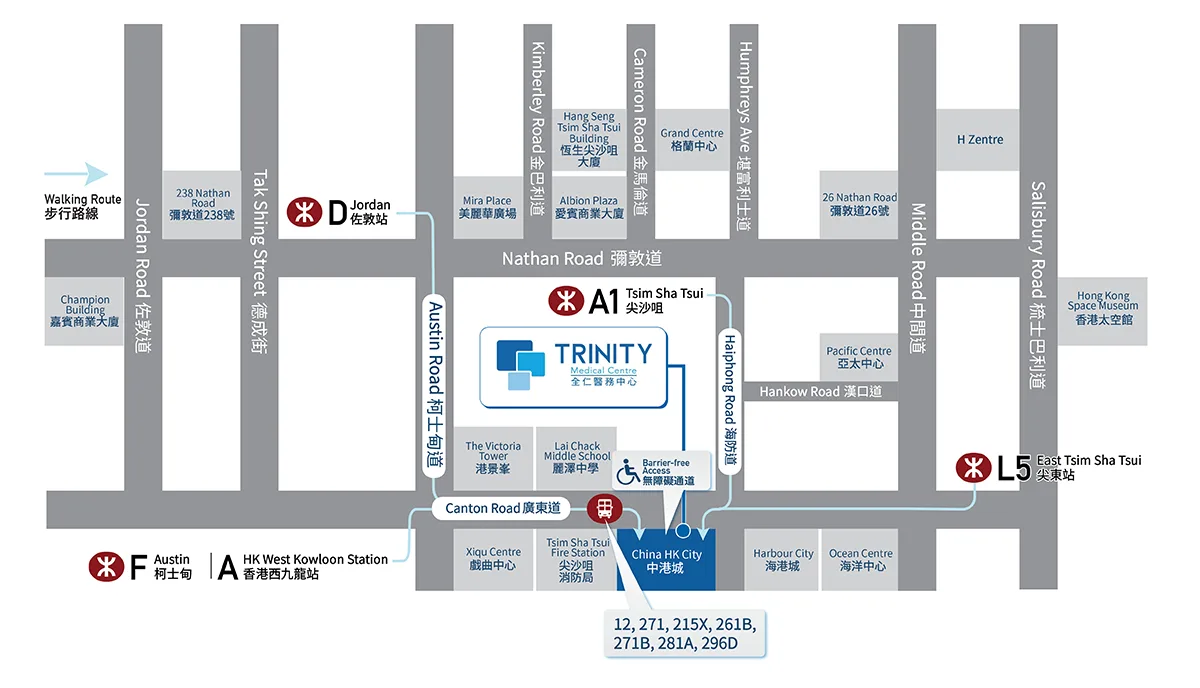
Tsim Sha Tsui – Trinity Diagnostic & Medical Centre
15/F, Tower 5, China Hong Kong City,
33 Canton Road, Tsim Sha Tsui, Kowloon
|
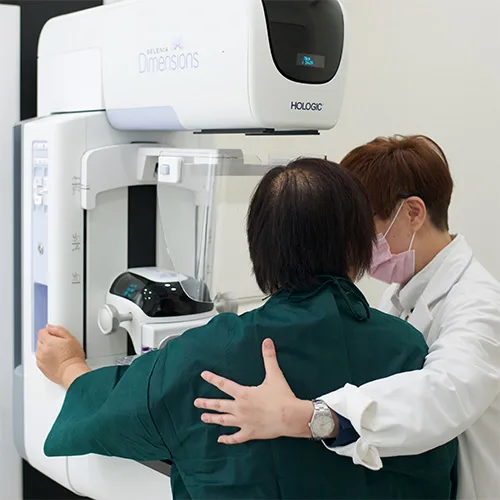
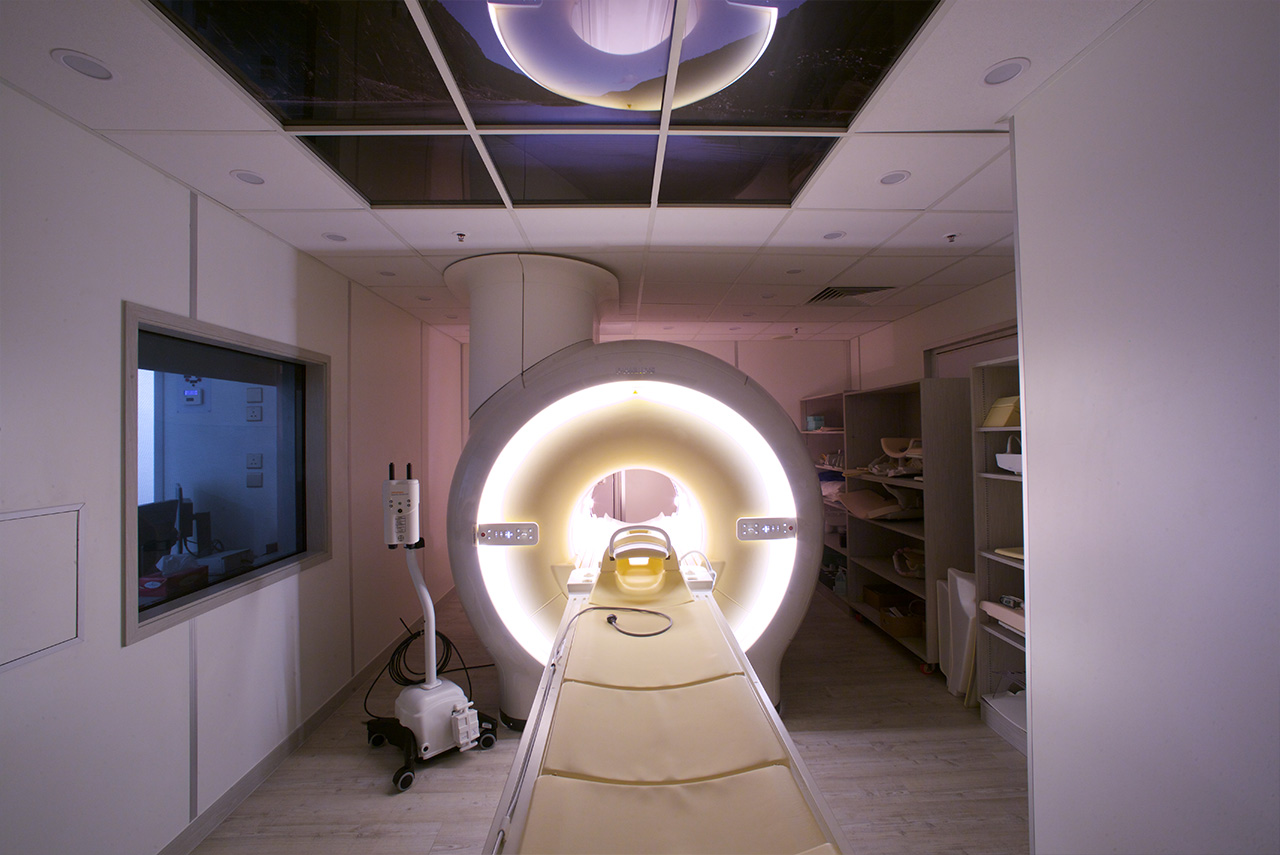
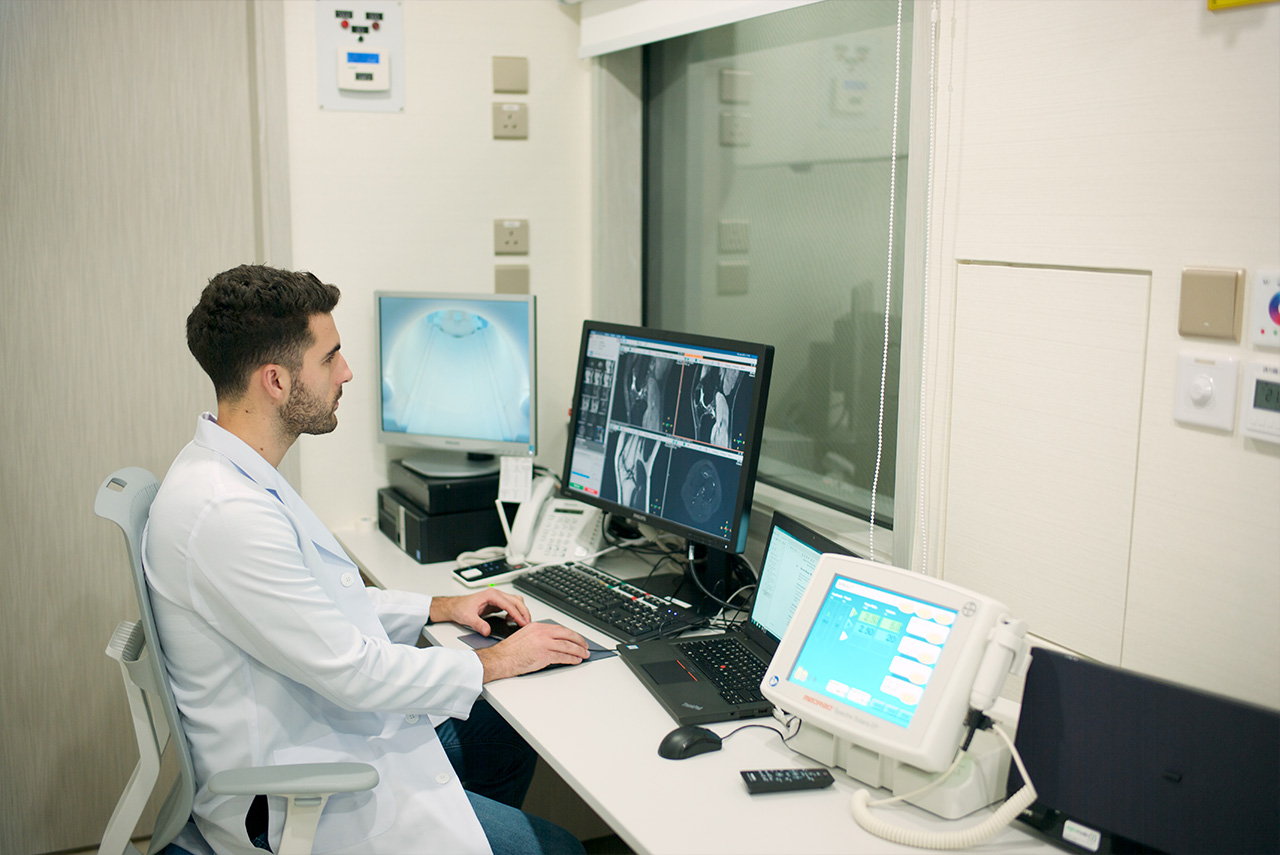
Diagnostic
Health Check
Booking and Enquiry:
Diagnostic Centre
Tel: 2197 0122
Fax: 2197 0199
Email: reception@trinitymedical.com.hk
WhatsApp: 6586 9522
Tel: 2197 0122
Fax: 2197 0199
Email: reception@trinitymedical.com.hk
WhatsApp: 6586 9522
Medical Centre (Check up, Vaccinations, Aesthetics)
Tel: 2192 7022
Fax: 2191 0082
Email: tmc@trinitymedical.com.hk
WhatsApp: 6062 8943
Tel: 2192 7022
Fax: 2191 0082
Email: tmc@trinitymedical.com.hk
WhatsApp: 6062 8943
About Us
Welcome to Trinity Medical Centre! We believe that healthier people makes a better world. We are dedicated to improve the health of the communities we serve by providing premier quality and affordable health care services with compassion, professionalism and integrity.